1.2.1 EXAMPLE: ANNUITY
Lotto Winnings: Lump Sum or an Annuity
|
I |
n March 2007, the Mega Millions lottery had
a $390 million jackpot, the largest in the world at the time.
The lottery winners had the choice of taking the payments
over time (an Annual Payout or annuity) or taking a single lump sum payment
(the Cash Option).
The annual payout was $15 million every year for 26 years.
The Cash Option was to receive an immediate payment of
$233 million.
If you were the winner, what would you do,
take the Annual Payout or the Cash Option?
Answering this question requires understanding the time value of money and taxes. In this topic we will ignore taxes and instead focus on the time value of money as captured by interest rates and annuities.
An
annuity is a series of fixed payments over time, such as the
Annual Payout from a lottery.
There are two types of annuities: ordinary
annuities and annuities in-advance.
In an ordinary annuity, you receive the payments at the
end of the period, e.g. at the end of the year.
With an annuity in-advance, you receive the payment at
the beginning of the period.
Lottery payouts are annuities in-advance; if you choose
the Annual Payout option, you get the first payment right away,
the next payment one year later, and so on.
The present value of the Annual Payout is given by the annuity formula (a derivation is in the appendix to this chapter). The formula says if you receive a constant payment C for t periods and the interest rate is r, then the present value P(C,t), of an ordinary annuity is
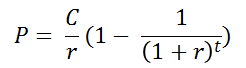
The present value of an
annuity-in-advance is C+P(C,t-1) since you get C immediately
and then C for t-1 more periods.
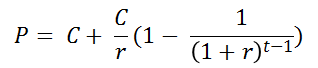
Refer now to the interactive calculator below
and assume that the interest rate is 6%.
Now you can compute the present value of $15m for 26 years,
for an in-advance annuity.
Using the calculator above you can check how changing the interest rate from 6% to a rate that is lower and then higher than 6% changes the present value of the prize and compare it to the lump sum option. If you check on "Calculate Implied Rate" you will see the interest rate that equates the present value of the annuity to the lump sum payment.
 office (412)
9679367
office (412)
9679367