CHAPTER 1: INTERACTIVE FTS
CASES
Interactive FTS
In an interactive FTS trading exercises you are part of the market's
trading crowd. You learn how to apply the concepts in
BondTutor from personal trading experience. In each FTS trading case the learning objectives are tied
to the price discovery problem. For example, the initial cases
emphasize the time value of money and market microstructure. The
Trading Screen Market Microstructure: The problem facing the market is to discover
the prices of these two securities as the market moves through time
with three trading periods. Period 1 is day 1 of year 1,
Period 2 is day 1 of year 2, and Period 3 is day 1 of year 3.
Trading is under the rules of the continuous
double auction institution. That is, unfilled bids are
continuously ranked from highest to lowest in the market book and
unflilled Asks are continuously ranked from lowest to highest in the
market book. There are three types of trades supported: 1. Market making limit order. For
this order you submit a Bid to buy some quantity at your specified
price or an Ask to sell some quantity at your specified price.
This order type appears in the book in the top RHS of the above
screen dump. 2. Market order. For this order
you are a market taker and submit a quantity to buy from an existing
Ask or sell to an existing Bid. The latest Market order
transaction appear under last in the top LHS of the above screen
dump. 3. Market limit order. For this
order you are a market taker and you submit a limiting price
and a quantity. That is, for a market limit buy order you are
attempting to buy from the best Ask so long as it is not higher than
the price you submit. A market limit sell order attemtps to
sell to best Bid so long as it is not lower than the price you
submit. This would also appear under Last in the above screen
dump if a market limit order was the most recent transaction. In the above you can be either of two types
of traders. A market maker who attempts to earn the spread but
cannot control execution, or a market taker who pays the spread but
controls execution. In the real world the market makers are
the primary dealers who can make market in Government securities. Long and Short Positions Your current position in a security appears as
either a positive or negative number under Position in the above
screen. Suppose you buy 10 coupon bonds and
hold them then at the end of each year your cash account is credited
with 10*$Coupon payment and at the end of .three year's you receive
10*$Coupon payment + 10 *Face Value. Each period the cash
earned will earn interest in your money market. At the time of
purchase your money market cash amount is reduced by 10*Purchase
Price. You can also sell bonds that you do not own!
This is known as short selling. Suppose you short 10 bonds you
do not currently own and maintain this short position.
Now you receive in your cash account 10*$Selling price but at the
end of each year you must cover the cash payments from the 10-bonds.
That is,at the end of year 1 10*$coupon payment is subtracted from
your account, etc., and at end of year 3 (10*$coupon payment +
10*$Face Amount) is automatically subtraqcted from your money market
account. If you are short any security then under
Positions above this would displayed as a negative number. In your money market account you can borrow
or lend and if you borrow you pay the money market rate in interest
at the end of each year and vice versa if you lend. By running through the interactive demo above
you will get to experience the actual dynamics of the market.
Exercise 1:
Trading Case B01
Case Objective
To understand the time value of money;
to understand the cash flows from coupon and zero coupon bonds; to
apply the discounting formula to value such bonds. To master the operational details associated
with trading bonds in a continuous double auction institution -- the
form used in the real world secondary trading markets. The
Primary dealers are the market makers and the retail general
investing public are the market takers. In this case you get
to play both roles -- Primary dealer as well as retail investor.
Key Concepts
Time value of money; discounting;
determining bond prices given interest rates. Textbook Integration:
Background Reading
Section 1.2 Present Value and inparticular
read the Three Period Example. In B01 this type of financial
problem faces the trading crowd in a market. That is, traders
are buying and selling fixed income securities with the objective
making money. In the next chapter of Bond Tutor you will
learn the finer points
associated with bond pricing.
The rules that govern trading in the market are
referred to as the market microstructure and these rules are
briefly described above and for additional details click on
market microstructure.
. Instructor References for the FTS
Interactive Markets Instructors can contact
ftsweb@gmail.com for additional
details regarding how you can get your class up and running with B01
and related bond trading cases.
Overview of FTS Interactive Markets
To get going (using either a Windows PC or a Mac) click on:
Important Note: To run the FTS Interactive Trader you need port
number 4502 open. If your firewall blocks this port then you
will need to skip this next link.
Once the FTS Interactive trader is loaded click on the button
"Connect to Demo."
Note: The demonstration trading case is B02 which is
introduced in Chapter 2, section 2.6 titled Interactive Cases.
This demonstration illustrates the screen elements, the market
microstrucutre as well as the dynamics of a FTS interactive trading
exercise.
Schools can contact ftsweb@gmail.com
for details as to how to get your classes up and running and
competing in a rice discovery trading exercise.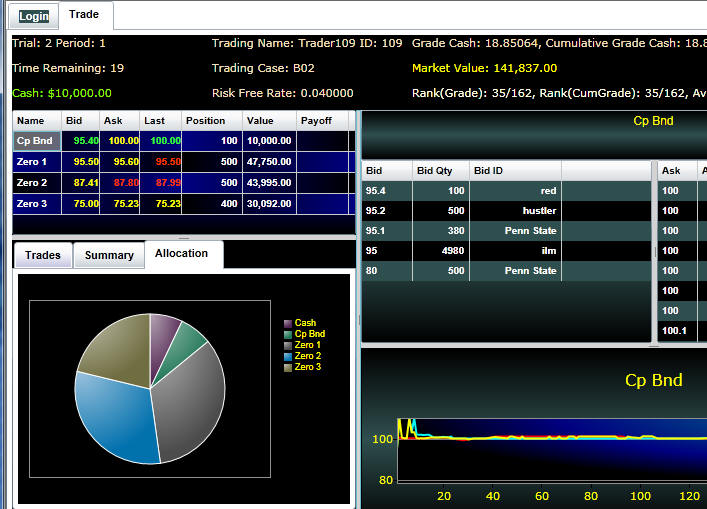
 office (412)
9679367
office (412)
9679367
email: ftsweb@gmail.com
toll-free 1 (800) 214-3480